AI Article Writer
Boost Your Organic Traffic by Writing SEO Optimized Articles 95% Faster!
Write 7 High Quality Articles for just $1 each!
Trusted by 40,000+ content writers worldwide!

Loving godlike mode man. Your tool is fucking amazing though mate. It’s ranking everywhere and for everything, e.g.my personal site, parasite seo, affilate articles etc. And it’s fast too! 🔗
Julian Goldie

Loving godlike mode man. Your tool is fucking amazing though mate. It’s ranking everywhere and for everything, e.g.my personal site, parasite seo, affilate articles etc. And it’s fast too! 🔗
Julian Goldie
Unique
Works for Any Niche!
Multiple Languages
Multiple Modes
- Quick Mode
- News Mode
- Godlike Mode
- Amazon Reviews
- Article Optimizer
- Bulk Generation
- AI Infographics
- Snippet Optimizer
- Advanced Settings
- Semantic SEO Analysis
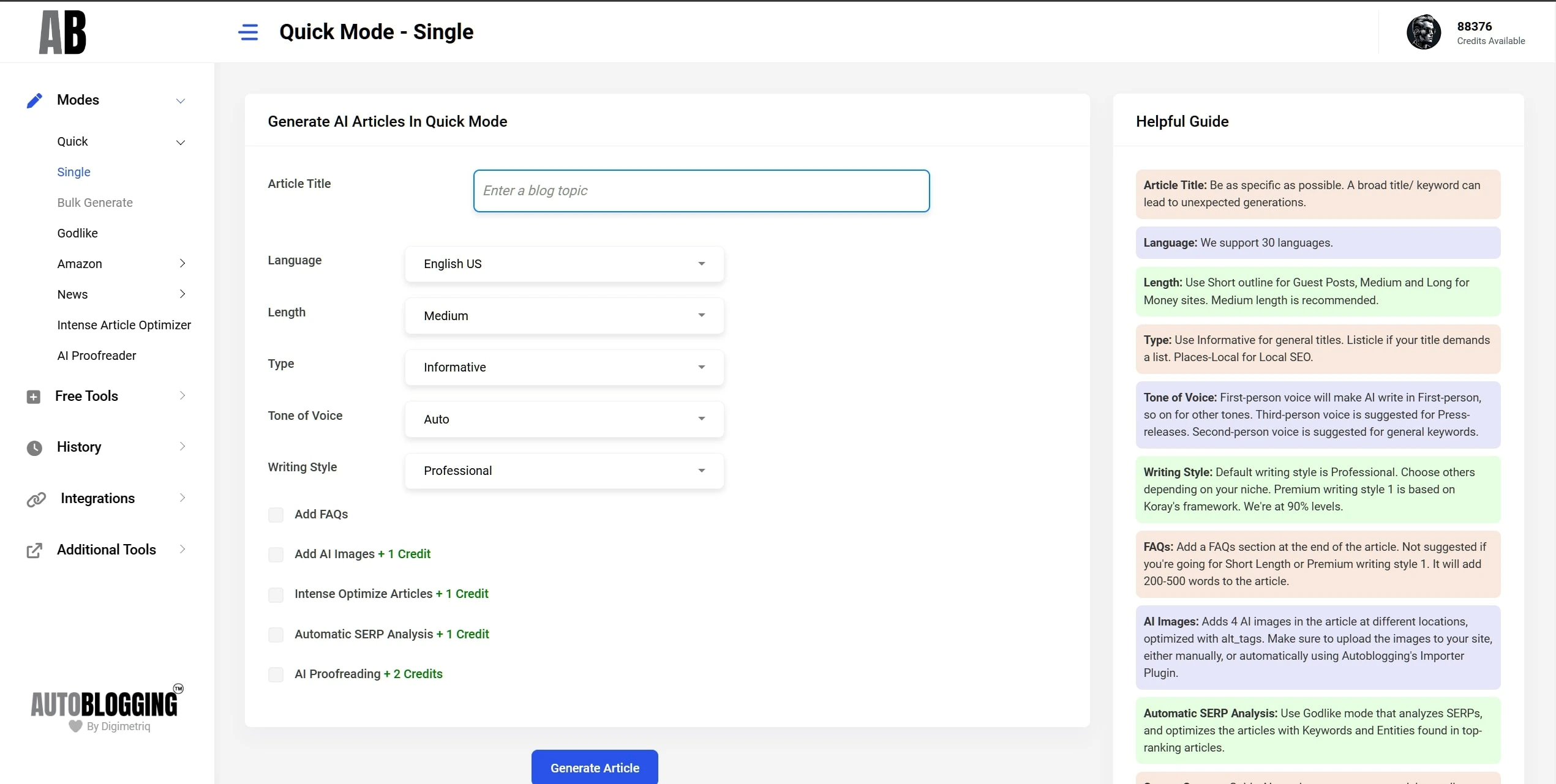
Quick Mode
Auto-pilot with Best Quality!
Generate High-quality SEO Optimised articles, hands-free and quickly!
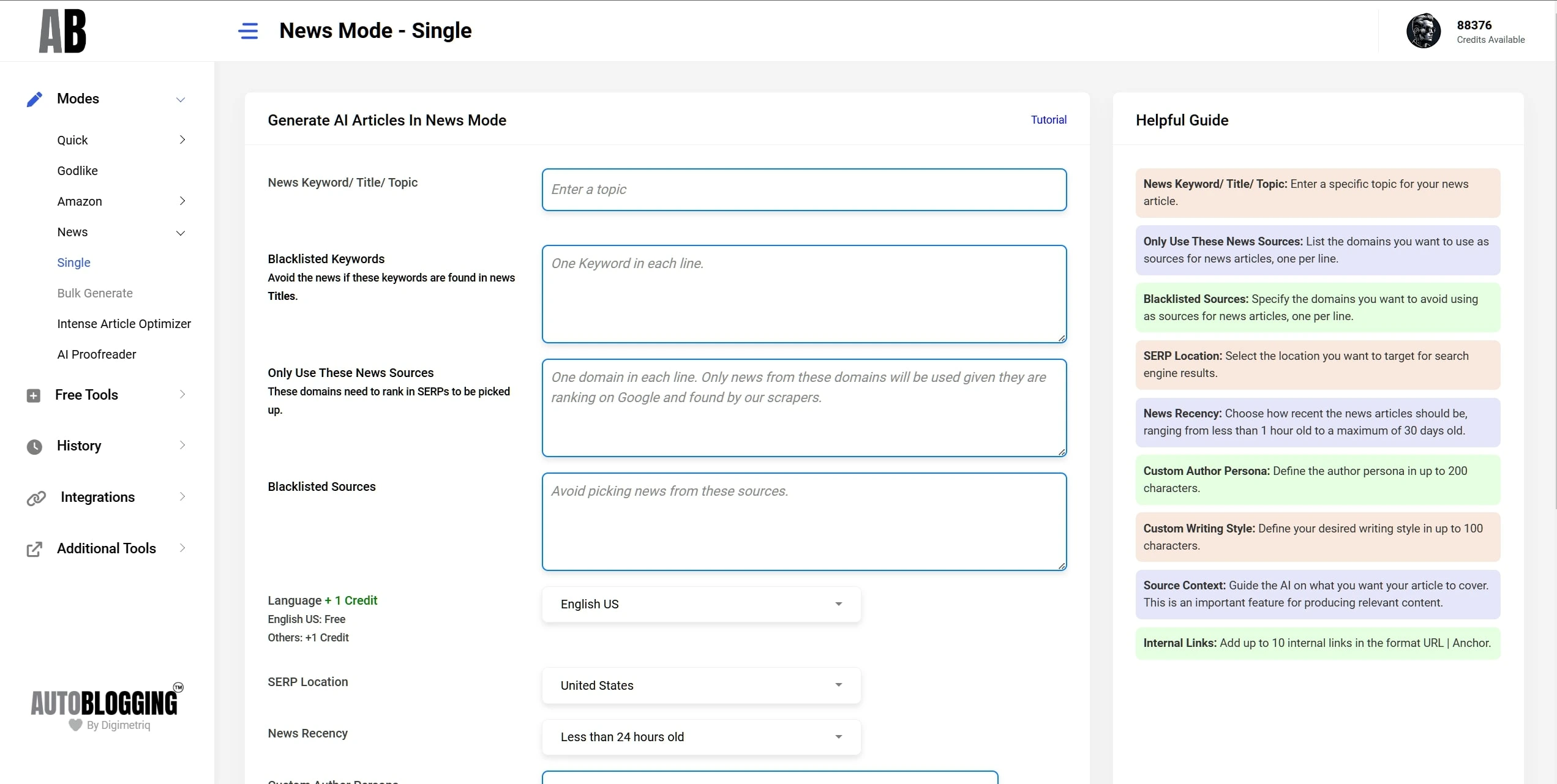
News Mode
No More Dormant Sites!
Generate and schedule future news articles for your sites.
Set-and-forget approach!
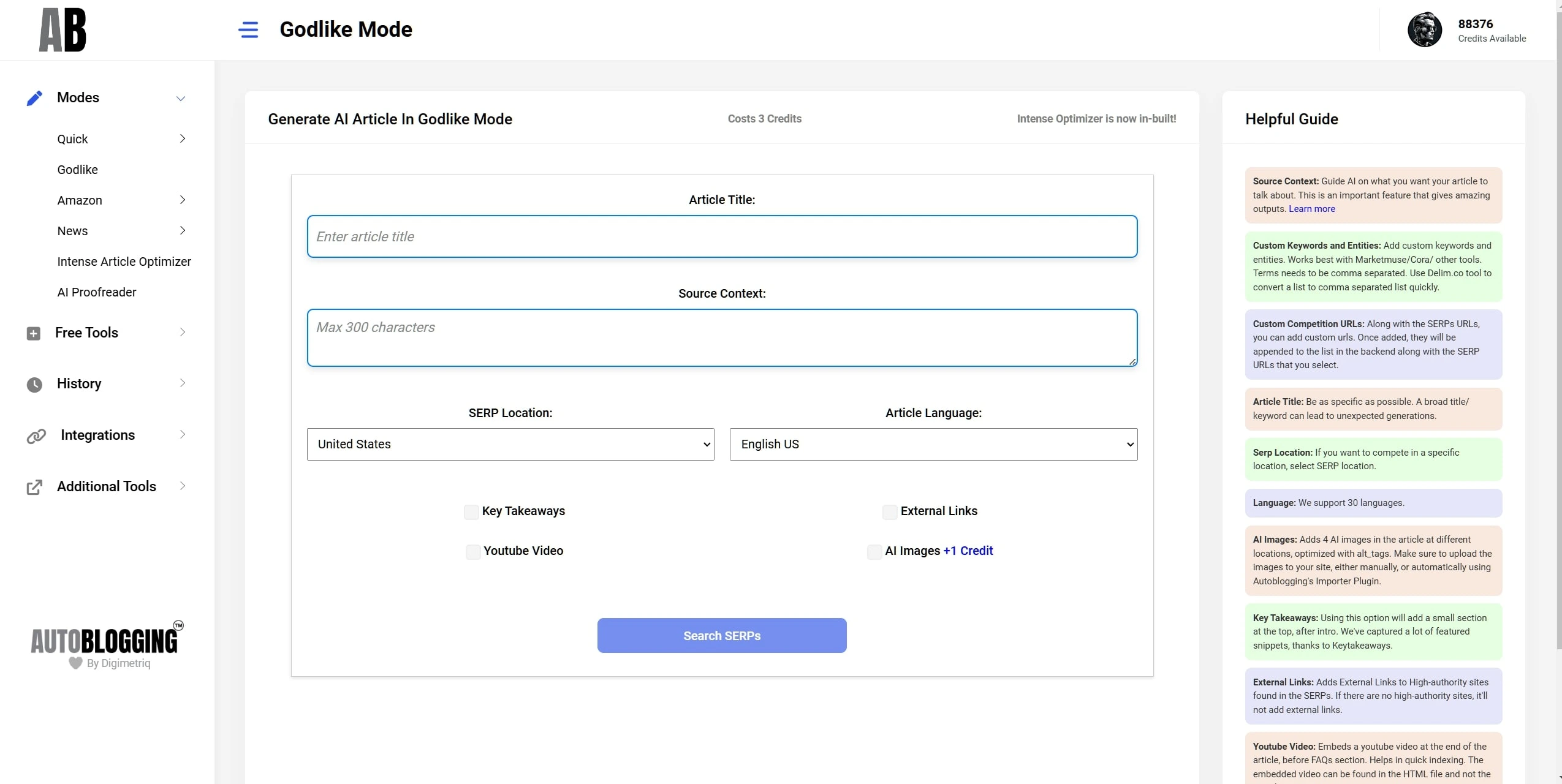
Godlike Mode
SERP Analysis!
Finds Keywords and Entities from SERPs and add videos, key takeaways, and external links.
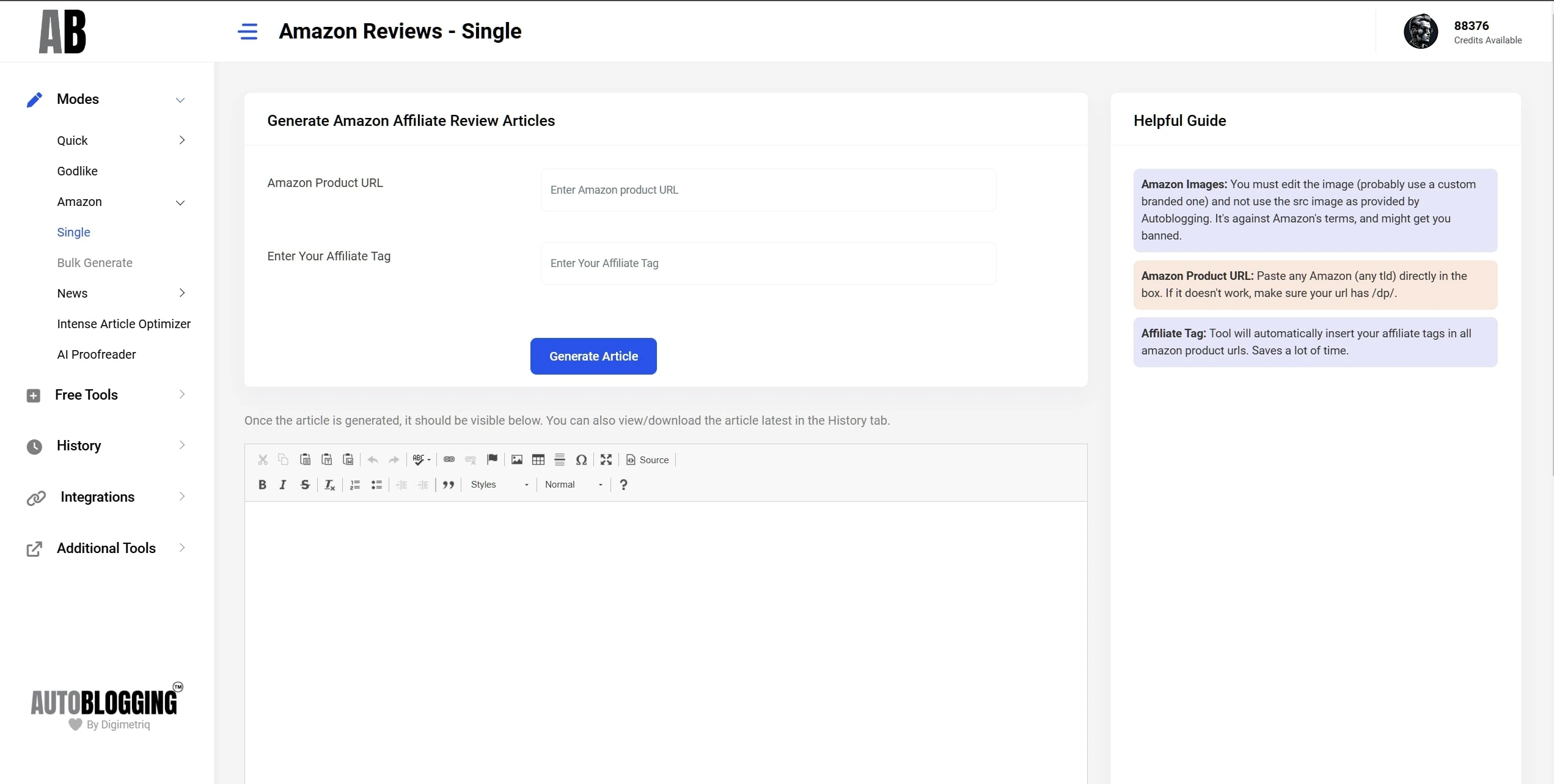
Amazon Reviews
Factually correct!
Generate the best personalised, review articles using any Amazon product URL!
Article Optimizer
SEO-optimize Articles
Use this mode to insert all keywords and entities in your existing articles.
Pretty intense!
Bulk Generation
Our USP!
Effortlessly handle bulk article creation and auto post to WP!
AI Infographics
AI Charts!
Add factually correct, AI Infographics in your Articles!
Help Google Crawlers find unique Information Gain when it visits your pages!
Semantic SEO Analysis
Detailed Analysis Report
A mode to check your Article against 21 Semantic SEO Principles within minutes!
Get actionable steps immediately to improve your article by 10x!
Features
Quick Mode
Auto-pilot with Best Quality!
Generate High-quality SEO Optimised articles, hands-free and quickly!
News Mode
No More Dormant Sites!
Generate and schedule future news articles for your sites.
Set-and-forget approach!
Godlike Mode
SERP Analysis!
Finds Keywords and Entities from SERPs and add videos, key takeaways, and external links.
Amazon Reviews
Factually correct!
Generate the best personalised, review articles using any Amazon product URL!
Article Optimizer
SEO-optimize Articles
Use this mode to insert all keywords and entities in your existing articles.
Pretty intense!
Bulk Generation
Our USP!
Effortlessly handle bulk article creation and auto post to WP!
AI Infographics
AI Charts!
Add factually correct, AI Infographics in your Articles!
Help Google Crawlers find unique Information Gain when it visits your pages!
Semantic SEO Analysis
Detailed Analysis Report
A mode to check your Article against 21 Semantic SEO Principles within minutes!
Get actionable steps immediately to improve your article by 10x!
Pricing
Regular
Get 720 credits immediately, valid for a year, with access to all features.
Free 60 minutes Strategy call
Standard
Get 1800 credits immediately, valid for a year, with access to all features.
Free 60 minutes Strategy call
Premium
Get 6000 credits immediately, valid for a year, with access to all features.
Free 60 minutes Strategy call
Starter
Regular
Standard
Premium
- Annual – Save 35%!
- Monthly
Regular
Get 720 credits immediately, valid for a year, with access to all features.
Free 60 minutes Strategy call
Standard
Get 1800 credits immediately, valid for a year, with access to all features.
Free 60 minutes Strategy call
Premium
Get 6000 credits immediately, valid for a year, with access to all features.
Free 60 minutes Strategy call
Starter
Regular
Standard
Premium
Pay-as-you-go Credits
Monthly credits expire every 30 days.
Annual credits, every 365 days.
Buy credits that do not expire, priced at $2/ credit.
How are credits used?
| Mode/Feature | Credits/Article |
|---|---|
| Quick, News & Amazon Mode | 1 Credit |
| Godlike Mode (Intense Article Optimizer In-built) | 2 Credits |
| Intense Article Optimizer | 1 Credit |
| AI Images | 1 Credit |
| Premium Writing Style/ Snippet Optimizer | Free |
| AI Proofreading | 1 Credit |

Done for you packages
A Done For You Service
Done for you packages
Delegate to our VAs!
With our Done for you plans, we can handle the automations and upload content to your site, while you focus on the other aspects.
Multiple Packs to choose from that does the following:
01. Bulk Generate
02.+ Auto Internal Linking
03. + Proof-reading
Our Team
Vaibhav Sharda
Scott Calland
Kasra Dash
Karl Hudson
James Dooley
Samples
Latest AI News
Powered by Autoblogging's News ModeWhat is Autoblogging?
In the digital age, content creation has evolved with the advent of AI technologies. One significant breakthrough in this domain is autoblogging, a method of generating blog content automatically. Autoblogging, also known as automatic blogging or automated blogging, leverages advanced software to create articles, eliminating the need for manual writing. This innovation has given rise to tools like autoblogging.ai, a leading name in the auto blogging software market.The Evolution of Auto Blogging Software
Originally, autoblogging was a simple process of aggregating content from different sources. However, with the integration of AI, autoblogging software like autoblogging.ai and autoblogger has become more sophisticated. These platforms use AI algorithms to generate unique and relevant content, transforming the concept of an auto blog writer into a reality.Autoblogging.ai Review
Among the various options, autoblogging.ai stands out. It has been praised for its efficient automatic blog writer capabilities. As an auto blogger, this platform offers a seamless experience in generating automatic blog posts, making it a favorite among users seeking an efficient auto ai writer. The autoblogging ai technology underpinning this platform ensures high-quality content generation.Features of Autoblogging Software
Key features of autoblogging software include automated blog writing, article generation, and scheduling of posts. Platforms like dash.buymorecredits.com and autoblogger nl offer these services, along with unique features like auto blog com and auto blogging wordpress integrations. The autoblogger plugin, particularly popular in the WordPress community, facilitates easy blog management.AI Blogging and Its Impact
AI blogging has revolutionized the way content is created. With ai auto write features, platforms like autoblogging samurai and wp auto blogger automate the entire content creation process. This includes automated article writing, a feature that allows for the generation of complete articles with minimal human input.Blogging with Artificial Intelligence
The core of AI blogging lies in ai blogging software, which powers the ai blogger. These tools are capable of understanding context and generating articles that are both relevant and engaging. AI auto writer technologies, including automatic writing website and blog ai writer features, are increasingly being adopted for their efficiency and time-saving benefits.The Rise of AI-Generated Blogs
The trend of ai generated blog and ai generated blogs is gaining momentum. Automatic ai writer tools are enabling even novice bloggers to produce content at an unprecedented scale. Automotive blogger platforms and other niche blogging sites are also adopting ai blog tools to enhance their content quality.Autoblogging Plugins and Tools
WordPress, being a popular blogging platform, offers a range of autoblogging plugin options like wordpress auto blogging. These plugins, such as autoblog wordpress, automate content generation, making it easier for bloggers to maintain a consistent posting schedule.Free AI Blogging Tools
The market also offers free blog writing ai tools. Platforms like ai blog post writer and wordpress autoblogging are making AI technology accessible to all bloggers. The ai automatic writing feature is particularly beneficial for those looking for a cost-effective solution.AI in Blog Writing
The integration of AI into blog writing has led to the development of ai writing blogs and ai for writing blog tools. These tools, including automatic writing ai and blog writer free options, are enhancing the blogging experience. Blog writing ai free tools are particularly popular among bloggers on a budget.The Future of AI Blogging
Looking ahead, the ai blog posts and automatic article writer technology will continue to evolve. The best ai blog writer tools will likely incorporate more advanced AI capabilities, making auto article writer and blog writer software even more sophisticated. Autoblogging.ai and similar platforms represent a significant advancement in content creation. The combination of ai writing blog and free blog writer ai tools is making blogging more accessible and efficient. As ai for blog posts technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions in the field of auto blogs and blog writing tool. The era of best ai blogs and ai bloggers is just beginning, and the potential for growth in this field is immense.Autoblogging.ai is a product of Digimetriq.com, the team behind innovative automation solutions for blogging. Our mission is to help bloggers, website owners and agencies save time and improve their online presence through cutting-edge technology.